If incoming governments in liberal democracies wish to use public contracts to benefit those loyal to them, they face institutional constraints. To implement corrupt procurement strategies they would need to sabotage these checks and balances. By comparing procurement data from Hungary and the UK, Liz Dávid-Barrett and Mihály Fazekas can identify the relative effect of such anti-democratic institutional changes, as seen in Hungary, on government patronage. Is liberalism really dead? In his […]
Using ‘red flag’ indicators to identify corruption and analyse reform efforts in the procurement process
Liz David-Barrett and Mihály Fazekas The campaign to open up contracting around the world has had a positive consequence for corruption researchers: there is an abundance of data about public procurement (government purchases of goods, works and services from an external source through a tendering process). In our GI-ACE project, we use this data to develop new proxy indicators of corruption risk, based on ‘red flags’ […]
Data update of World Bank, IADB, and EuropeAid datasets on development aid funded contracts and projects
We are releasing an update on the datasets collected on development projects, public tenders, and contracts for three major donor agencies: the World Bank, the Inter-American Development Bank (IADB), and EuropeAid. The datasets not only republish structured data gathered from official source websites, but also contain corruption risk red flags developed by the research team. About the project We analyse how procurement can be manipulated […]
Workshop in Uganda explores new data
On 13-14 October, Liz David-Barrett ran a workshop together with the Department of Mathematics at Makerere University, Uganda, and the African Maths Initiative on Analysing Corruption Risks in Procurement Data. The workshop brought together top Maths and Statistics students with civil society experts on anti-corruption in Uganda to analyse data and look for ‘red flags’ of corruption risk. As well as using open-source statistics software […]
Anti-corruption interventions in development aid: Is corruption reduced or merely displaced?
Most anti-corruption interventions are small-scale and targeted. Hence, there is a risk that they simply displace corruption rather than reducing it as corrupt actors adapt to the new conditions. Direct attempts at improving corruption controls in one area might elicit two evasive tactics: corrupt actors could shift focus to areas with weaker controls or could more aggressively exploit the loopholes that remain. Observing such displacement […]
Brown Bag Lunch presentation at the Inter-American Development Bank
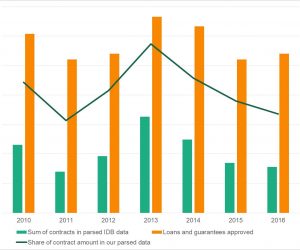
This BBL delivered by Mihály Fazekas showcased the power of Big Data for detecting corruption risks, put forward recommendations on IDB data collection, and demonstrated some of the successful examples of anticorruption tools and interventions enabled by our new datasets and corruption risk indicators. The BBL provided an overview of IDB, World Bank and donor agencies’ public procurement datasets and links to other data such as […]
Data publication: public procurement in Tanzania, 2009-2016
This publication contains Tanzanian public procurement data retrieved from the issues of Tanzania Procurement Journal between 2009 and 2016. The dataset was compiled as a part of the research project ‘Quantitative corruption analysis: implementation and case study’ with the ultimate aim of exploring ways to increase transparency and integrity through Big Data solutions. The research project was carried out by researchers from the Mathematical Institute […]
Policy Brief: Data infrastructure in Tanzania
The publication of data about government procurement is widely perceived to be beneficial in terms of improving transparency over a significant area of public spending. Transparency in public procurement is associated with greater scrutiny over processes and outcomes, helping to improve accountability in order to achieve enhanced competition, better value for money and reduced corruption. In 2017, as part of a project on Statistics for […]
Policy Brief: Recommendations for donors
This short Policy Brief introduces and explains our red flags method for analysing corruption risks in aid spent through national procurement systems, and offers some recommendations to donors on how best to curb corruption. We propose three main recommendations: (1) Invest in building better data infrastructure. Not only can this help donors control aid, but it can also empower civil society groups, provide leads for investigative journalists […]
Datasets for download: World Bank, IADB, and EuropeAid
Here you can find the full datasets collected on development projects, public tenders, and contracts for 3 major donor agencies: the World Bank, the Inter-American Development Bank, and EuropeAid. The project was supported by the British Academy/ UK Department for International Development Anti-Corruption Evidence Programme. The final datasets result from a concerted effort by the University of Sussex, Government Transparency Institute, and Datlab. In addition […]