Fazekas, M., Dávid-Barret, E., Abdou, A., Basdevant, O. (2020). The Corruption Cost Tracker: Quantifying the costs of corrupt contracting and the savings to be made from reform. GTI-R/2020:02, Budapest: Government Transparency Institute. Public procurement constitutes about one-third of government spending or 13 trillion USD per year. It is highly vulnerable to corruption with estimates of losses amounting to 10-20%. Corruption in public procurement can lead to: […]
Anti-corruption in aid-funded procurement: Is corruption reduced or merely displaced?
David-Barrett E. and Fazekas, M. (2020). Anti-corruption in aid-funded procurement: Is corruption reduced or merely displaced? World Development. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2020.105000 Given a widespread sense among donors that mainstream anti-corruption reforms over the past 25 years have failed to yield results, there is a move towards more targeted interventions. Such interventions should, in principle, overcome implementation gaps and make it easier to evaluate impact, supporting learning. […]
Building public procurement integrity in Jamaica
Written by Elizabeth David-Barrett and originally published on the ACE-Global Integrity blog. Public procurement is one of the key ways of corruptly channelling money out of the state, not least because it is one of the few areas of public spending in which there is significant discretion. That means that, in a well-functioning state, there will be many bodies with an interest in controlling and overseeing […]
India’s federal procurement data infrastructure
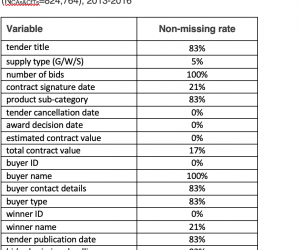
Written by Isabelle Adam and published on the ACE-Global Integrity blog. In a previous blog, we explored some common problems data scientists encounter when collecting and analyzing data. In the accompanying Red Flags Explainer, we drew on our experience of building and analysing datasets of government procurement over the past ten years to answer some Frequently Asked Questions about our work, explaining some of the challenges and what […]
India’s Federal Procurement Data Infrastructure: Observations and Recommendations
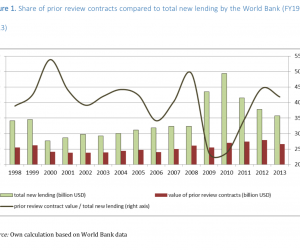
Improving transparency in public procurement, that is publishing more and better-quality data, supports accountability by enabling greater scrutiny over processes and outcomes as well as helping to achieve greater competition and better value for money. In India, according to the Ministry of Finance General Financial Rules (2017), all procuring authorities are responsible and accountable for ensuring transparency, fairness, equality, competition and appeal rights in contracting. […]
Measuring the benefits of open contracting: Case studies on Mexico, Paraguay, and Slovakia
Adam, I., Fazekas, M. & Tóth, B. (2020). Measuring the benefits of open contracting: Case studies on Mexico, Paraguay, and Slovakia. GTI-WP/2020:01, Budapest: Government Transparency Institute. Enhancing the transparency of government in general and of public procurement processes in particular has been increasingly on the agenda of governments, civil societies and businesses as evidenced by initiatives such as the Open Government Partnership which has seen 70 […]
Where does pressure for public procurement transparency come from? Reflections from Uganda and Tanzania
Written by Isabelle Adam and originally published on the ACE-Global Integrity blog. For years, the benefits of transparency as a policy tool to increase accountability and counter corruption have been lauded. In public procurement, this has given rise to a global movement promoting procurement data transparency, a.k.a. open contracting. Many governments have committed to making public procurement data more transparent and open for public scrutiny. But […]
Why is collecting and analysing data about public procurement so damned difficult? Data scientists explain some common problems
Written by Elizabeth David-Barrett and originally published on the ACE-Global Integrity blog. Open data is often lauded as a magic pill for anti-corruption: reveal what’s going on, inform the public, and, presto, government will become more accountable. Oh, and big data just means bigger gains, right? Not quite. We have written elsewhere about the institutional and political challenges that can hinder the transparency –> accountability transformation. But […]
Grand corruption and the authoritarian turn
If incoming governments in liberal democracies wish to use public contracts to benefit those loyal to them, they face institutional constraints. To implement corrupt procurement strategies they would need to sabotage these checks and balances. By comparing procurement data from Hungary and the UK, Liz Dávid-Barrett and Mihály Fazekas can identify the relative effect of such anti-democratic institutional changes, as seen in Hungary, on government patronage. Is liberalism really dead? In his […]
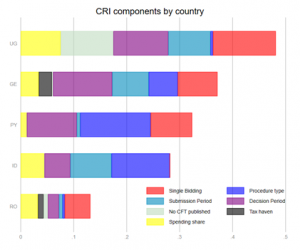
Using ‘red flag’ indicators to identify corruption and analyse reform efforts in the procurement process
Liz David-Barrett and Mihály Fazekas The campaign to open up contracting around the world has had a positive consequence for corruption researchers: there is an abundance of data about public procurement (government purchases of goods, works and services from an external source through a tendering process). In our GI-ACE project, we use this data to develop new proxy indicators of corruption risk, based on ‘red flags’ […]