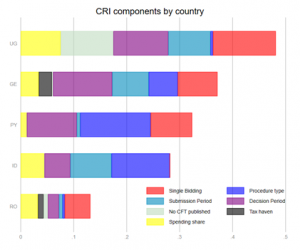
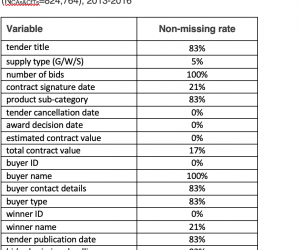
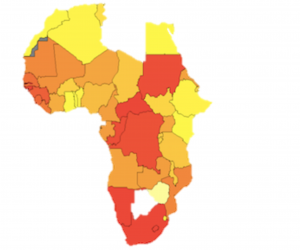
Fazekas, M., Dávid-Barret, E., Abdou, A., Basdevant, O. (2020). The Corruption Cost Tracker: Quantifying the costs of corrupt contracting and the savings to be made from reform. GTI-R/2020:02, Budapest: Government Transparency Institute. Public procurement constitutes about one-third of government spending or 13 trillion USD per year. It is highly vulnerable to corruption with estimates of losses amounting to 10-20%. Corruption in public procurement can lead to: […]
India’s Federal Procurement Data Infrastructure: Observations and Recommendations
Improving transparency in public procurement, that is publishing more and better-quality data, supports accountability by enabling greater scrutiny over processes and outcomes as well as helping to achieve greater competition and better value for money. In India, according to the Ministry of Finance General Financial Rules (2017), all procuring authorities are responsible and accountable for ensuring transparency, fairness, equality, competition and appeal rights in contracting. […]
Policy Brief: Data infrastructure in Tanzania
The publication of data about government procurement is widely perceived to be beneficial in terms of improving transparency over a significant area of public spending. Transparency in public procurement is associated with greater scrutiny over processes and outcomes, helping to improve accountability in order to achieve enhanced competition, better value for money and reduced corruption. In 2017, as part of a project on Statistics for […]
Policy Brief: Recommendations for donors
This short Policy Brief introduces and explains our red flags method for analysing corruption risks in aid spent through national procurement systems, and offers some recommendations to donors on how best to curb corruption. We propose three main recommendations: (1) Invest in building better data infrastructure. Not only can this help donors control aid, but it can also empower civil society groups, provide leads for investigative journalists […]